SERVICES
SERVICES
Our featured services are designed to empower farmers and policy makers with the tools and knowledge they need to succeed in today’s dynamic agricultural landscape. Whether you’re looking to optimize farm productivity, improve environmental sustainability, or develop evidence-based policies, our comprehensive range of services has you covered. Partner with us to unlock the full potential of your agricultural initiatives and policy decisions.
Agriculture
Our agriculture focused services utilize advanced geospatial technology to optimize farming practices, increase crop yields, and ensure sustainable agriculture.
Precision Agriculture
- Description: Leverage our precision agriculture services to implement data-driven farming techniques. Tailor farming practices to specific field conditions using geospatial data.

- Need: Precision agriculture enhances resource use efficiency, reduces environmental impact, and increases farm profitability.
Soil Analysis
- Description: Conduct comprehensive soil mapping and fertility analysis using geospatial data. Understand soil composition, nutrient levels, and moisture content to optimize soil management practices.

- Need: Soil analysis is crucial for maintaining soil fertility, improving crop productivity, and preventing nutrient imbalances.
Our agriculture focused services utilize advanced geospatial technology to optimize farming practices, increase crop yields, and ensure sustainable agriculture.
Crop Type Mapping
- Description: Identify and map different crop types within your fields using advanced remote sensing and GIS technology.

- Need: Accurate crop type mapping is essential for planning crop rotations, managing diverse cropping systems, and making informed decisions on resource allocation.
Crop Intensity Mapping
- Description: Analyze and visualize the intensity of crop growth and productivity across your fields.
- Need: Crop intensity mapping helps in optimizing input application, improving yield forecasting, and identifying areas requiring special attention.
Crop Health Monitoring
- Description: Monitor the health and vigor of crops using remote sensing technologies such as NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) and other vegetation indices.
- Need: Regular monitoring of crop health is crucial for early detection of stress factors, enabling prompt and effective management to ensure healthy crop growth.
Our agriculture focused services utilize advanced geospatial technology to optimize farming practices, increase crop yields, and ensure sustainable agriculture.
Crop Suitability Analysis
- Description: Assess the suitability of different crops for specific areas based on soil, climate, and other geospatial data.

- Need: Crop suitability analysis helps farmers select the most appropriate crops for their land, thereby maximizing productivity and minimizing risk.
Yield Mapping
- Description: Collect and analyze yield data to create detailed maps of crop production across your fields.

- Need: Yield mapping provides insights into spatial variability in crop production, helping farmers understand the performance of different field zones and optimize future planting and management strategies.
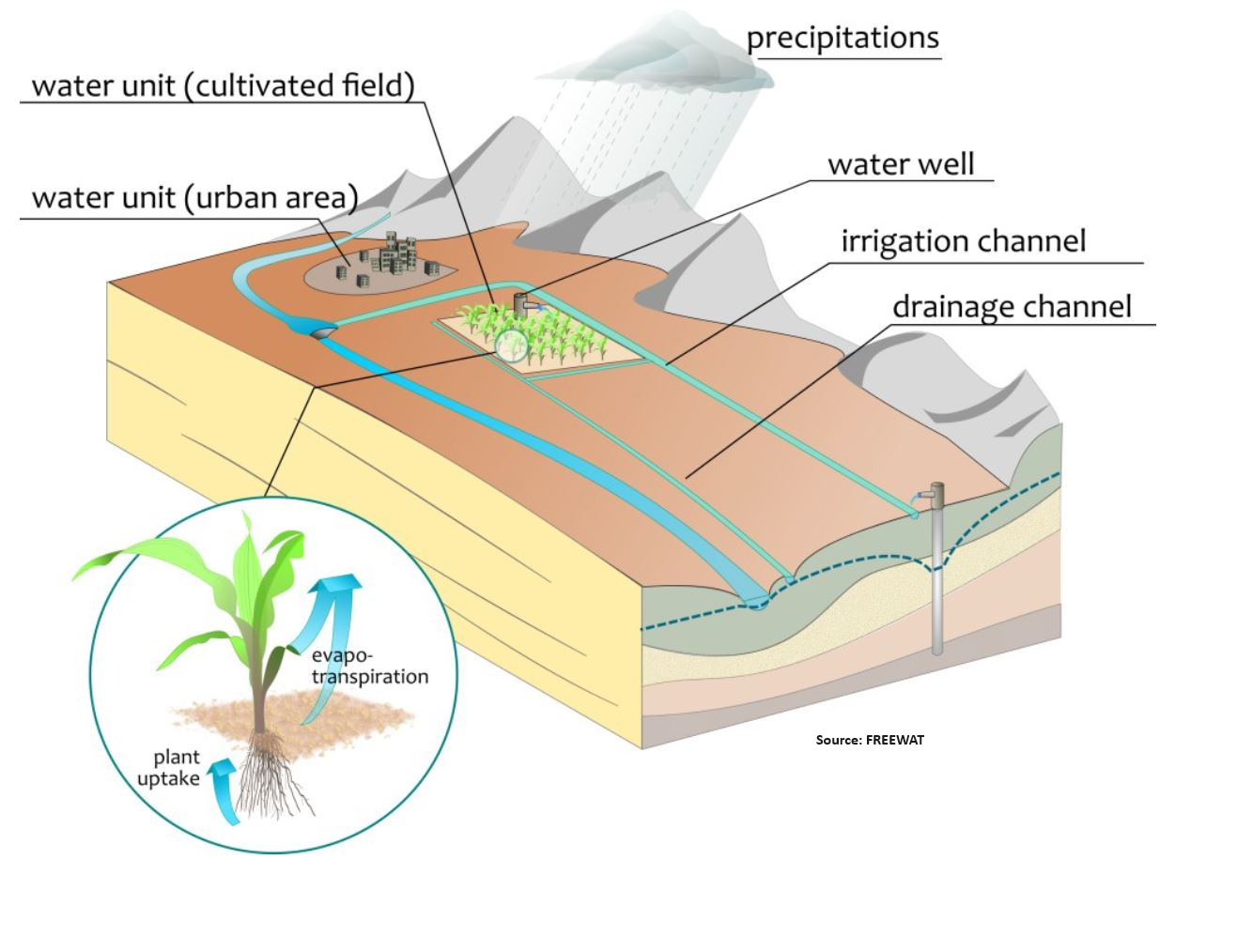
Water
Description: Our water related services focus on efficient water management, irrigation optimization, and water resource conservation using geospatial technology.
Water Quality Monitoring
Description: Monitor water quality parameters such as pH, EC, and nutrient levels to ensure water suitability for irrigation and agricultural use.
Examples:
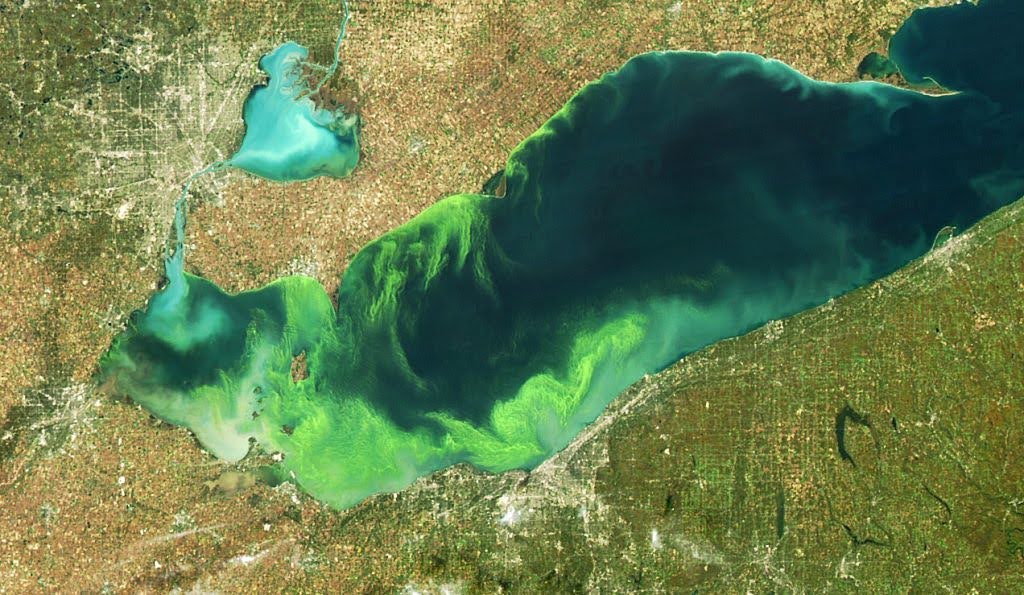
Surface Water Monitoring: Using satellite imagery to detect algal blooms and pollution in surface water bodies that may affect irrigation water quality.
Groundwater Assessment: Conducting groundwater surveys and analysis to assess water quality and availability for irrigation purposes.
Need: Monitoring water quality is essential for preventing contamination, ensuring crop health, and maintaining the sustainability of water resources.

Description: Our water related services focus on efficient water management, irrigation optimization, and water resource conservation using geospatial technology.
Irrigation Management
Description: Optimize irrigation practices with realtime monitoring and precision irrigation techniques. Reduce water waste, improve water use efficiency, and ensure optimal crop growth.
Examples:
Irrigation Scheduling: Using soil moisture sensors and satellite data to schedule irrigation based on actual crop water needs.
Drip Irrigation Design: Designing drip irrigation systems based on topographic data and soil characteristics to minimize water usage.
Need: Efficient irrigation management is critical for maximizing crop yields, conserving water resources, and mitigating water related risks such as droughts and salinization.

Description: Our water related services focus on efficient water management, irrigation optimization, and water resource conservation using geospatial technology.
Hydrology Analysis
Description: Conduct hydrological analysis using GIS technology to assess water availability, runoff patterns, and watershed characteristics for informed water resource management.
Examples:
Watershed Delineation: Using GIS tools to delineate watershed boundaries and analyze the flow of water within a catchment area.
Flood Risk Mapping: Mapping floodprone areas based on topographic data, land use, and rainfall patterns to identify areas at risk and develop mitigation strategies.
Need: Hydrology analysis provides valuable insights into water distribution, flood risk assessment, and watershed management, helping to ensure sustainable water resource use and management.
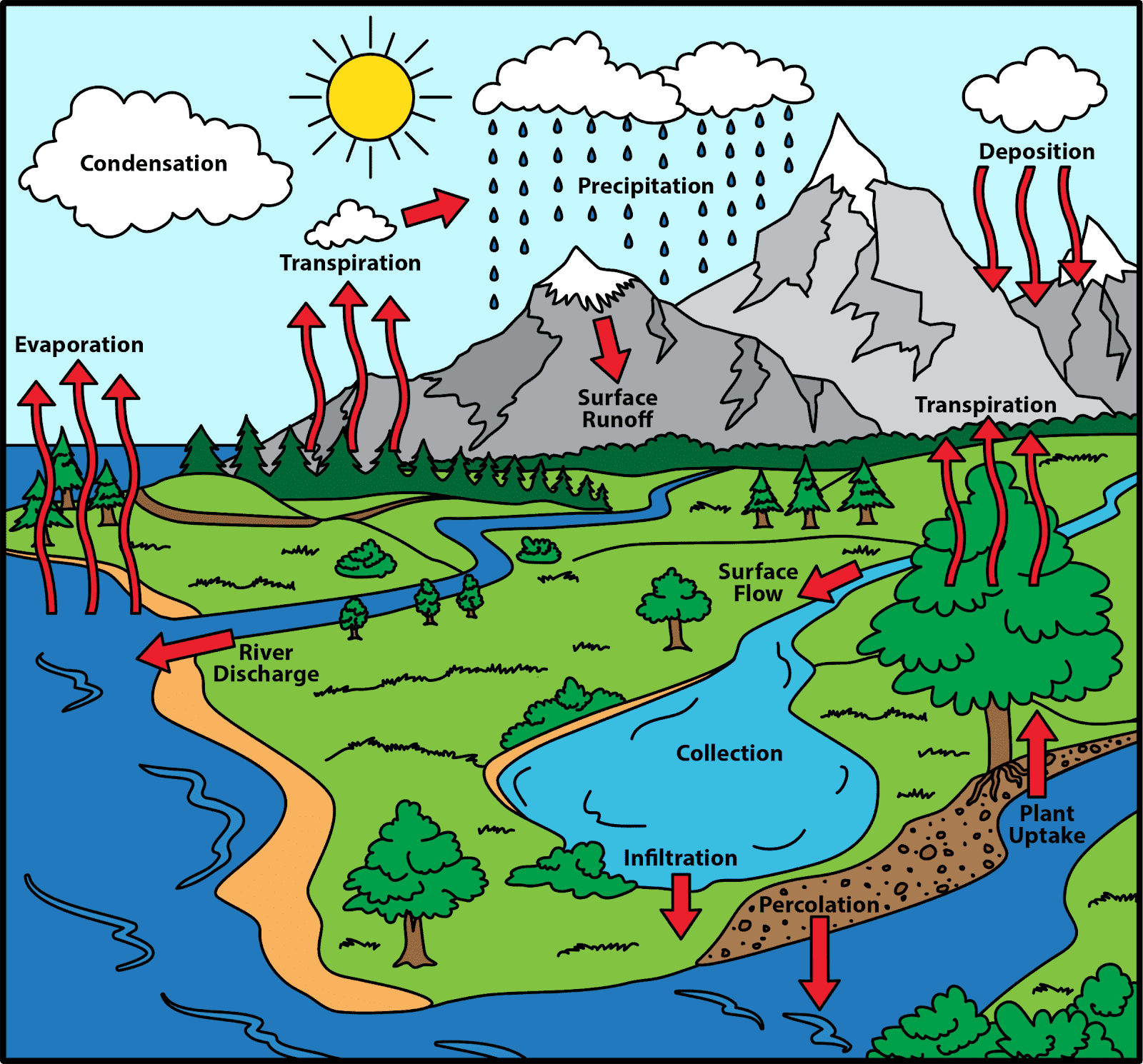
Description: Our water related services focus on efficient water management, irrigation optimization, and water resource conservation using geospatial technology.
Water Resource Modelling
Description: Develop hydrological models using GIS technology to simulate water flow, groundwater recharge, and water balance dynamics for effective water resource planning and management.
Examples:
Hydrological Modeling: Developing rainfallrunoff models to simulate streamflow and assess the impact of land use changes on water availability.
Water Balance Analysis: Analyzing water inputs, outputs, and storage within a hydrological system to evaluate water resource sustainability and identify management strategies.
Need: Water resource modeling enables stakeholders to make informed decisions about water allocation, infrastructure development, and drought preparedness, contributing to longterm water security and resilience.
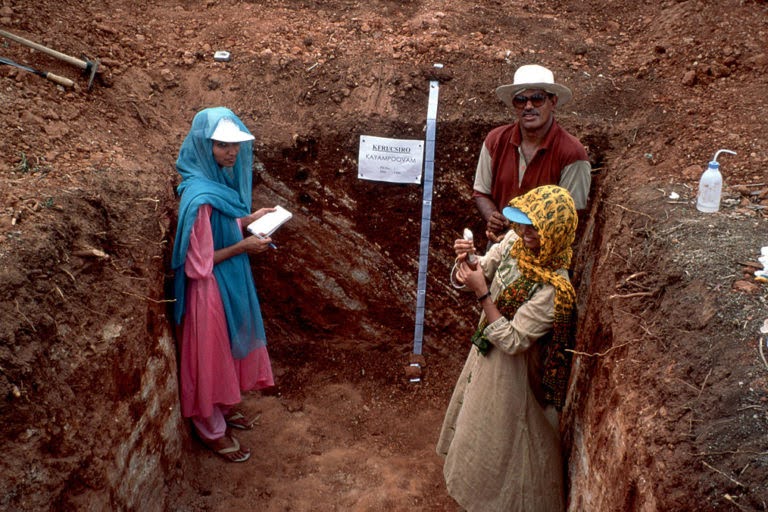
Surveying
Description: Our surveying services provide accurate and detailed data collection for various agricultural applications, including land mapping, soil analysis, and crop monitoring.
- Soil Surveying
- Description: Perform comprehensive soil surveys to analyze soil properties, fertility, and health for optimal crop management and soil conservation.
- Benefits: Understand soil composition, identify nutrient deficiencies, and implement targeted soil management practices.
- Examples:
- Soil Sampling: Collecting soil samples at different depths and locations to assess soil texture, pH, and nutrient levels.
- Erosion Mapping: Mapping soil erosion hotspots using imagery to prioritize soil conservation measures.
- Need: Soil surveying provides valuable information for land suitability assessment, crop selection, and erosion control practices.

Description: Our surveying services provide accurate and detailed data collection for various agricultural applications, including land mapping, soil analysis, and crop monitoring.
- Land Surveying
- Description: Conduct detailed land surveys to map field boundaries, topography, and infrastructure for efficient land use planning and management.
- Benefits: Establish clear field boundaries, plan infrastructure development, and optimize land use.
- Examples:
- Boundary Mapping: Surveying field boundaries and property lines to establish land ownership and prevent encroachments.
- Topographic Mapping: Creating digital elevation models (DEMs) to assess terrain characteristics and plan land leveling activities.
- Need: Accurate land surveying is essential for land tenure security, land-use planning, and precision agriculture applications.

Description: Our surveying services provide accurate and detailed data collection for various agricultural applications, including land mapping, soil analysis, and crop monitoring.
- Land Surveying
- Description: Carry out crop surveys to assess crop health, growth stages, and yield potential. Crop surveys provide critical data for effective crop management and yield optimization.
- Benefits: Monitor crop performance, detect issues early, and make timely interventions to enhance crop health and productivity.
- Examples:
- Growth Stage Monitoring: Tracking the growth stages of crops to ensure they are developing as expected and to identify any issues early.
- Yield Estimation: Estimating potential crop yields based on field surveys and remote sensing data.
- Need: Crop surveying is essential for effective crop management, enabling farmers to monitor crop performance, detect issues early, and take corrective actions to maximize yields.

Description: Our surveying services provide accurate and detailed data collection for various agricultural applications, including land mapping, soil analysis, and crop monitoring.
- Hydrological Surveying
- Description: Conduct hydrological surveys to analyze water resources, assess water availability, and manage water-related risks. Hydrological surveys are crucial for effective water resource management and flood risk assessment.
- Benefits: Ensure sustainable water use, mitigate flood risks, and enhance water resource planning.
- Examples:
- Watershed Analysis: Surveying watersheds to understand water flow patterns and manage water resources effectively.
- Flood Risk Assessment: Identifying flood-prone areas and developing flood mitigation plans based on hydrological surveys.
- Need: Hydrological surveying is essential for managing water resources sustainably, mitigating flood risks, and ensuring the resilience of agricultural systems to water-related challenges.
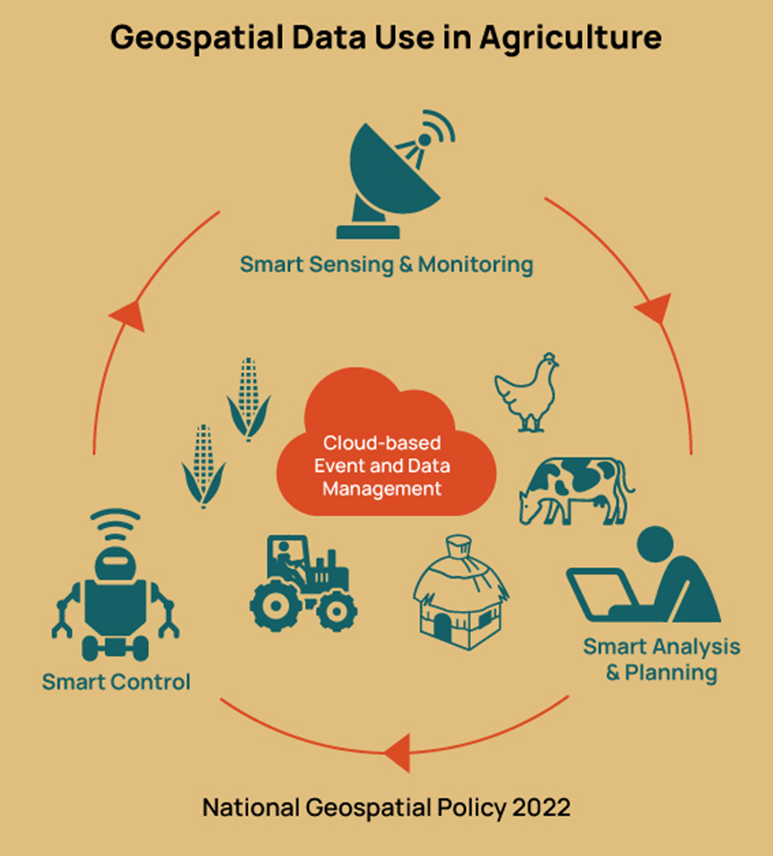
Big Data, AI, and Data Science
Description: Leverage the power of big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and data science to unlock actionable insights from geospatial data. Our advanced analytics and machine learning models support informed decision-making and enhance agricultural productivity.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Description: Implement AI technologies to automate processes, enhance decision-making, and provide real-time insights. AI algorithms can process complex datasets and identify patterns that are not immediately apparent to human analysts.
- Benefits: Increase operational efficiency, reduce human error, and enhance predictive capabilities.
- Examples:
- Precision Agriculture: Using AI-driven tools to analyze real-time data from drones and IoT sensors to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: AI-powered systems that adjust irrigation schedules based on real-time soil moisture and weather data.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using AI to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur.
- Need: AI technologies enable farmers to optimize operations, improve resource management, and respond proactively to changing conditions, thereby enhancing overall farm productivity and sustainability.

Description: Leverage the power of big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and data science to unlock actionable insights from geospatial data. Our advanced analytics and machine learning models support informed decision-making and enhance agricultural productivity.
- Big Data Analytics
- Description: Collect, process, and analyze vast amounts of geospatial data to uncover trends, patterns, and insights that drive efficient and sustainable farming practices.
- Benefits: Identify key factors affecting crop performance, optimize resource use, and predict future trends.
- Examples:
- Crop Yield Prediction: Using historical yield data, weather patterns, soil health, and other environmental variables to predict future crop yields.
- Market Analysis: Analyzing market trends and commodity prices to inform planting decisions and optimize revenue.
- Pest and Disease Forecasting: Utilizing large datasets from various sources, including satellite imagery and weather data, to predict pest and disease outbreaks.
- Need: Big data analytics is crucial for making data-driven decisions that enhance productivity, reduce costs, and increase resilience to environmental and market fluctuations.

- Data Science
- Description: Apply data science methodologies to extract valuable insights from complex geospatial datasets. Data science techniques, including statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling, help in understanding and solving agricultural challenges.
- Benefits: Gain deeper insights, improve decision-making, and develop innovative solutions to agricultural problems.
- Examples:
- Soil Health Analysis: Using data science to analyze soil samples and predict nutrient deficiencies, guiding targeted soil amendment strategies.
- Climate Impact Modeling: Developing models to predict the impact of climate change on crop production.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Analyzing data across the supply chain to identify inefficiencies and optimize logistics.
- Need: Data science provides the tools to analyze complex agricultural data, enabling farmers to make informed decisions, innovate, and stay competitive in the rapidly evolving agricultural sector.

- Geospatial Data Integration
- Description: Integrate various geospatial data sources, including satellite imagery, drone data, and ground-based sensors, to create comprehensive datasets for analysis.
- Benefits: Provide a holistic view of the farm, improve data accuracy, and support complex analyses.
- Examples:
- Integrated Farm Management Systems: Combining data from multiple sources to provide a unified view of farm operations.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Assessing the impact of farming practices on the environment by integrating land use data, water usage statistics, and biodiversity indicators.
- Disaster Response Planning: Using integrated geospatial data to develop plans for responding to natural disasters such as floods and droughts.
- Need: Integrating geospatial data enhances the accuracy and reliability of analyses, providing farmers with a detailed understanding of their operations and enabling better decision-making.
Contact Agritech Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
Get in Touch: Contact form for inquiries, partnerships, collaborations, and policy consultations.
Let’s Start a Conversation
Ready to transform agriculture and shape evidence-based policies for a sustainable future? Get in touch with us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you achieve your agricultural and policy goals. Whether you have a question, need assistance, or want to explore partnership opportunities or policy consultations, our team is here to help. Connect with us via email, phone, or social media to start the conversation.
Agritech Innovations Pvt. Ltd.
Unit A – 205, Sri Lakshmi Shubham Arcade
Chanda Nagar, Hyderabad – 500 050
Phone: +91-8019793112
Email: connect@agritechinn.com
Web: www.agritechinn.com
